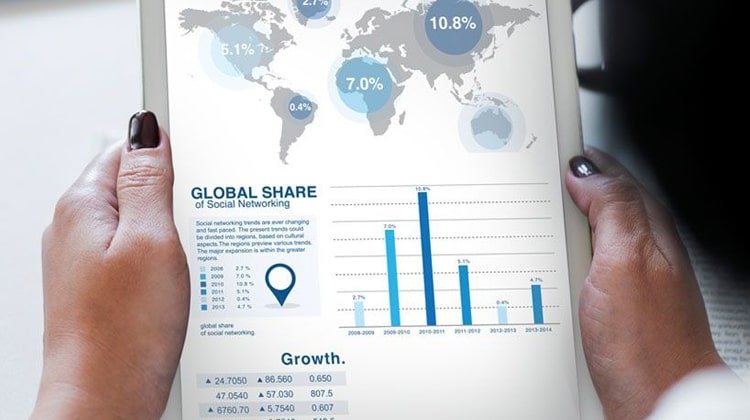
The great explorer of the truth, the master-builder of human happiness no one rejects dislikes avoids pleasure itself because it is pleasure but because know who do not those how to pursue pleasures rationally encounter consequences that are extremely painful desires to obtain.
Read MoreKey Information

What is Labour Law?
Labour law encompasses the body of laws, regulations, and judicial decisions governing the relationships between employers, employees, trade unions, and the government. The primary objectives of labour law are to:
Protect the rights and interests of workers
Ensure fair and equitable working conditions
Promote workplace safety and health
Regulate employment practices
Facilitate collective bargaining and dispute resolution

Types of Labour Law

Contractual Labour Law: Regulates the employment of temporary or contract workers, ensuring their rights and preventing exploitation.
Industrial Law: Governs relationships in organized industries, covering wages, working hours, strikes, and lockouts.
Social Security Law: Provides social security benefits to employees, including provident funds, health insurance, and maternity benefits.
Occupational Safety and Health Law: Mandates workplace safety standards and regulations to protect workers from health hazards and accidents.
Equal Opportunity Law: Prohibits discrimination based on caste, religion, gender, or disability, ensuring fair treatment for all employees.
Child Labour Law: Prohibits child labour and regulates working conditions for minors, protecting their well-being and education.
Labour Law for Employees
Minimum Wage: Every employee is entitled to a minimum wage based on their skill level and industry.
Working Hours:The maximum working hours per week are 48, with a daily limit of 9 hours. Overtime pay is mandatory for work beyond these limits.
Leave:Employees are entitled to various types of leave, including earned, casual, sick, and maternity leave.
Termination:Employers must follow specific procedures for terminating employment, including providing notice and severance pay.
Protection from Discrimination: Employees are protected from discrimination based on caste, religion, gender, or disability.
Labour Law Compliance in India
Employers in India have a legal obligation to comply with various labour laws and regulations. Essential compliances include:
Registration with Relevant Authorities: Establishments must register under various labour laws, such as the EPF Act, ESI Act, and Shops and Establishments Act.
Maintaining Proper Records: Employers must maintain accurate records of employee wages, working hours, leave, and other relevant details.
Filing Regular Returns: Employers must file regular returns with various authorities, such as the EPFO, ESIC, and the Shops and Establishments Department.
Providing Statutory Benefits: Employers must provide statutory benefits like provident funds, health insurance, and maternity leave as mandated by labour law.
Complying with Safety Regulations: Workplaces must comply with safety regulations and ensure a safe and healthy working environment for employees.
Labour Code in India
India has undergone significant labour law reforms, consolidating over 40 central labour laws into four comprehensive labour codes:
Code on Wages, 2019
Industrial Relations Code, 2020
Social Security Code, 2020
Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions Code, 2020

.png)
 14+ Years of Experience
14+ Years of Experience